- Vacuum Arc
in cooperation with High Current Electronics Institute Sibirian Division Russian Academy of Sciences, Tomsk
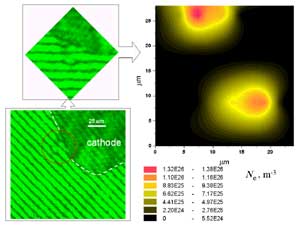 |
Interferogram and surface plot of electron density in cathode spot fragment, obtained for graphite cathode at arc current 30 A |
 |
Picosecond laser pulses at wavelength of 1064 nm have been focused onto copper cathode in coincidence with electric fields to produce laser-induced breakdown in vacuum. At power densities of about formation of the local regions with high pressures and temperatures in cathode micro-volume was investigated. As a result of an intensive energy deposition in small volume a strongly coupled cathode micro-plasma was formed, which properties varied during non-stationary processes of heating and hydrodynamic motion over a wide range of the phase diagram : from a Fermi-like to an ideal plasma. |
 |
The cathode spot formation in air within the first 170 ns was investigated by laser absorption photography and ps-pulse interferometry. The discharge wss initiated between electrodes made from Ag or Pd with cathode-anode distance below 300 µm, the arc duration was some mil1iseconds, and the arc current 5-10 A. Picosecond holographic interferometry and momentary absorption photography yielded spatial-temporal density distributions in the ignition phase of the cathode spot An absolute electron density value on the order of 4 x 1026 m-3 has been found. In contrast to vacuum, the cathode spot plasmas broaden little with increasing distance from the cathode, thus narrow plasma channels are observed in the vicinity of the cathode surface having diameters < 20 µm |
 We present results where highly supersonic plasma jets and accelerated plasma fragments are generated by interaction of intense laser pulse with a metallic target (Al, Cu, Ta, W) in gas atmosphere (air, Ar). The formation of jets and well-localized plasma „balls“ occur, when a strong forward shock (v ~ 107 cm/s) from a main laser pulse and a reverse shock from a prepulse meet together. Interferometric and shadowgraphic measurements with high temporal (100 ps) and spatial resolution (1 µm) yield information about the formation and evolution of plasma jets and plasma „balls“. Measurements of a self-generated magnetic field in supersonic plasma jets by means of Faraday-rotation showed, that the collimation of jets and fast acceleration of plasma fragments occur due to pinch-effect in plasma jets and JxB – force in front of shock impact We present results where highly supersonic plasma jets and accelerated plasma fragments are generated by interaction of intense laser pulse with a metallic target (Al, Cu, Ta, W) in gas atmosphere (air, Ar). The formation of jets and well-localized plasma „balls“ occur, when a strong forward shock (v ~ 107 cm/s) from a main laser pulse and a reverse shock from a prepulse meet together. Interferometric and shadowgraphic measurements with high temporal (100 ps) and spatial resolution (1 µm) yield information about the formation and evolution of plasma jets and plasma „balls“. Measurements of a self-generated magnetic field in supersonic plasma jets by means of Faraday-rotation showed, that the collimation of jets and fast acceleration of plasma fragments occur due to pinch-effect in plasma jets and JxB – force in front of shock impact |
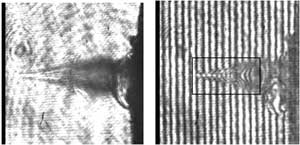 |
Fig. demonstrates the evolution of electron density profile for delay time t = 130 ps between pump and probe pulses. |
 Temporal evolution of x-ray radiation from plasma of low-voltage laser-induced discharges was investigated by means of picosecond x-ray streak camera with a temporal resolution of order of 20 ps. Intensive point-like structures of x-ray radiation with a life time of 250 ps to 1.5 ns and temperature > 100 eV, as well as radiation related to an expanding hot layer, which propagates with a velocity of 1.5 km/s to 5 km/s, were found in low current vacuum discharge (I = 2 - 35 A) initiated by picosecond laser beam. The radiation of laser-induced breakdown was investigated with a long delay time (up to 30 ns) relative to an ignition point by a laser beam in order to eliminate the x-ray radiation coming from the laser-produced plasma. Temporal evolution of x-ray radiation from plasma of low-voltage laser-induced discharges was investigated by means of picosecond x-ray streak camera with a temporal resolution of order of 20 ps. Intensive point-like structures of x-ray radiation with a life time of 250 ps to 1.5 ns and temperature > 100 eV, as well as radiation related to an expanding hot layer, which propagates with a velocity of 1.5 km/s to 5 km/s, were found in low current vacuum discharge (I = 2 - 35 A) initiated by picosecond laser beam. The radiation of laser-induced breakdown was investigated with a long delay time (up to 30 ns) relative to an ignition point by a laser beam in order to eliminate the x-ray radiation coming from the laser-produced plasma.
|



 We present results where highly supersonic plasma jets and accelerated plasma fragments are generated by interaction of intense laser pulse with a metallic target (Al, Cu, Ta, W) in gas atmosphere (air, Ar). The formation of jets and well-localized plasma „balls“ occur, when a strong forward shock (v ~ 107 cm/s) from a main laser pulse and a reverse shock from a prepulse meet together. Interferometric and shadowgraphic measurements with high temporal (100 ps) and spatial resolution (1 µm) yield information about the formation and evolution of plasma jets and plasma „balls“. Measurements of a self-generated magnetic field in supersonic plasma jets by means of Faraday-rotation showed, that the collimation of jets and fast acceleration of plasma fragments occur due to pinch-effect in plasma jets and JxB – force in front of shock impact
We present results where highly supersonic plasma jets and accelerated plasma fragments are generated by interaction of intense laser pulse with a metallic target (Al, Cu, Ta, W) in gas atmosphere (air, Ar). The formation of jets and well-localized plasma „balls“ occur, when a strong forward shock (v ~ 107 cm/s) from a main laser pulse and a reverse shock from a prepulse meet together. Interferometric and shadowgraphic measurements with high temporal (100 ps) and spatial resolution (1 µm) yield information about the formation and evolution of plasma jets and plasma „balls“. Measurements of a self-generated magnetic field in supersonic plasma jets by means of Faraday-rotation showed, that the collimation of jets and fast acceleration of plasma fragments occur due to pinch-effect in plasma jets and JxB – force in front of shock impact 
 Temporal evolution of x-ray radiation from plasma of low-voltage laser-induced discharges was investigated by means of picosecond x-ray streak camera with a temporal resolution of order of 20 ps. Intensive point-like structures of x-ray radiation with a life time of 250 ps to 1.5 ns and temperature > 100 eV, as well as radiation related to an expanding hot layer, which propagates with a velocity of 1.5 km/s to 5 km/s, were found in low current vacuum discharge (I = 2 - 35 A) initiated by picosecond laser beam. The radiation of laser-induced breakdown was investigated with a long delay time (up to 30 ns) relative to an ignition point by a laser beam in order to eliminate the x-ray radiation coming from the laser-produced plasma.
Temporal evolution of x-ray radiation from plasma of low-voltage laser-induced discharges was investigated by means of picosecond x-ray streak camera with a temporal resolution of order of 20 ps. Intensive point-like structures of x-ray radiation with a life time of 250 ps to 1.5 ns and temperature > 100 eV, as well as radiation related to an expanding hot layer, which propagates with a velocity of 1.5 km/s to 5 km/s, were found in low current vacuum discharge (I = 2 - 35 A) initiated by picosecond laser beam. The radiation of laser-induced breakdown was investigated with a long delay time (up to 30 ns) relative to an ignition point by a laser beam in order to eliminate the x-ray radiation coming from the laser-produced plasma.