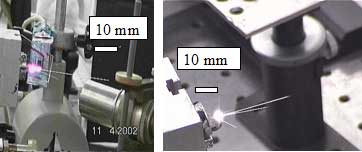
| We present results where highly supersonic plasma jets and accelerated plasma fragments are generated by interaction of intense laser pulse with a metallic target (Al, Cu, Ta, W) in gas atmosphere (air, Ar). The formation of jets and well-localized plasma „balls“ occur, when a strong forward shock (v ~ 107 cm/s) from a main laser pulse and a reverse shock from a prepulse meet together. Interferometric and shadowgraphic measurements with high temporal (100 ps) and spatial resolution (1 µm) yield information about the formation and evolution of plasma jets and plasma „balls“. Measurements of a self-generated magnetic field in supersonic plasma jets by means of Faraday-rotation showed, that the collimation of jets and fast acceleration of plasma fragments occur due to pinch-effect in plasma jets and JxB – force in front of shock impact |
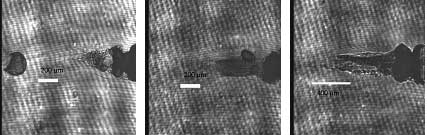
Shadowgramms of plasma "balls" and plasma jets
for delay time t = 375 ps after ignition by main pulse
Time-intergrated images of accelerated plasma fragments from laser-produced plasmas
References: